Mesothelioma Medications
FDA-approved mesothelioma medications for first-line treatment of the cancer include Opdivo (nivolumab) and Yervoy (ipilimumab). Combining mesothelioma drugs, such as chemotherapy and immunotherapy, can help some patients live longer.
What Drugs Are Approved for Mesothelioma?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved 5 drugs to treat pleural mesothelioma in adults. These mesothelioma medications aren’t intended to be used alone. Your doctor will consider several types of mesothelioma medications. They’ll use this information to decide the best treatment for you.
Chemotherapy drugs are the most commonly prescribed cancer treatment. These mesothelioma drugs kill cancer cells. They stop their growth and the cell division that leads to the disease’s spread. Immunotherapy drugs can help your body’s own immune system fight cancer.
FDA-Approved Medications for Mesothelioma
- Cisplatin with Alimta (Pemetrexed): The FDA-approved this combo of chemo drugs for mesothelioma in 2004.
- Keytruda (Pembrolizumab) with Chemo: The FDA-approved this immunotherapy drug with Alimta and platinum chemo as a first-line mesothelioma treatment in 2024.
- Yervoy (Ipilimumab) with Opdivo (Nivolumab): The FDA-approved this immunotherapy combo as a first-line treatment for mesothelioma in 2020.
Targeted therapy drugs stop the molecules that tell cancer cells to grow and spread. Anti-angiogenesis drugs stop nutrients and oxygen from reaching tumors. They starve cancer cells and prevent their growth. Photodynamic therapy drugs use light to destroy cancer cells after making the cells sensitive to light.
Some patients may also take medications the FDA hasn’t specifically approved for mesothelioma yet. These drugs may be available in clinical trials and compassionate-use programs. Speak to your mesothelioma doctor for information about participating in drug trials.
Chemotherapeutic Medications for Mesothelioma
Chemotherapy has side effects, but it’s one of the best ways to treat mesothelioma. Chemo drugs target and destroy fast-growing cells, like cancer cells. Your chemo treatment depends on the type of mesothelioma you have.
Pleural mesothelioma treatment usually involves standard chemo. It’s given through an IV infusion for several hours once every 21 days. Doctors may require you to undergo 2 to 4 cycles. More cycles may be necessary depending on the effectiveness of the treatments. Different chemo drugs may be prescribed if the cancer returns.
Common Chemotherapy Medications for Mesothelioma
- Alimta (Pemetrexed)
- Carboplatin
- Cisplatin
- Doxorubicin
- Gemcitabine
- Navelbine
- Pegargiminase
- Raltitrexed
Peritoneal mesothelioma treatment often involves surgery plus chemo. HIPEC, or hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy, involves tumor-removing surgery and then a heated chemo wash of the abdomen. Chemo drugs kill cancer cells better when heated.
Some commonly prescribed chemo drugs aren’t specifically FDA-approved for mesothelioma. Navelbine (vinorelbine) and gemcitabine, for example, are used alone or with other chemo drugs. Carboplatin is usually better tolerated than cisplatin with fewer severe side effects. Doxorubicin can be used with other chemo drugs. Its use is limited, however, because it can damage heart muscle tissue.
The Future of Chemo for Mesothelioma
Many new chemo-based therapies are regularly tested in clinical trials. The results of a breakthrough trial published in 2024 found combining the drug ADI-PEG20 (pegargiminase) with chemo significantly improves survival in people with pleural mesothelioma. Pegargiminase is the first drug in 20 years to be used with chemo. It’s hailed as a breakthrough. The trial found the mesothelioma drug increased median survival 1.6 months and quadrupled survival rates at 36 months.
Other clinical trials starting soon will study the safety and effectiveness of cadonilimab. This antibody will be combined with gemcitabine, Navelbine or Alimta. Another trial is testing Lenvima (lenvatinib) with Keytruda and chemo in pleural mesothelioma patients. It will check for effectiveness and risks.
Side Effects of Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs
Chemo drugs for mesothelioma can cause fatigue, nausea, hair loss, stomach pain and irregular stools. Medications are available to control these side effects. Contact your doctor if you notice serious side effects. These include a rash, chills, fever, swollen ankles or blood in your urine.
Mesothelioma expert Dr. Andrea Wolf says, “Sleep, good nutrition and recognizing that this is a long haul and that it’s normal are essential.” Pleural mesothelioma survivor Kim Madril says of her own experience, “The way I deal with fatigue is I try to get sleep. I try to eat a healthy diet.”
Common Side Effects of Mesothelioma Chemo Drugs
- Bleeding
- Bruising
- Fatigue
- Hair Loss
- Impaired vision or hearing
- Nausea
Taking the chemo drugs Alimta, carboplatin or cisplatin may harm your kidneys. The risk of harm increases if you take some medications. These include NSAIDs like aspirin, ibuprofen and naproxen. Your risk may also increase if you take certain antibiotics, antiviral or antiretroviral drugs, or some osteoporosis drugs. Tell your doctor what medications you’re using before chemo. That includes supplements and vaccines.
Mesothelioma Immunotherapy Drugs
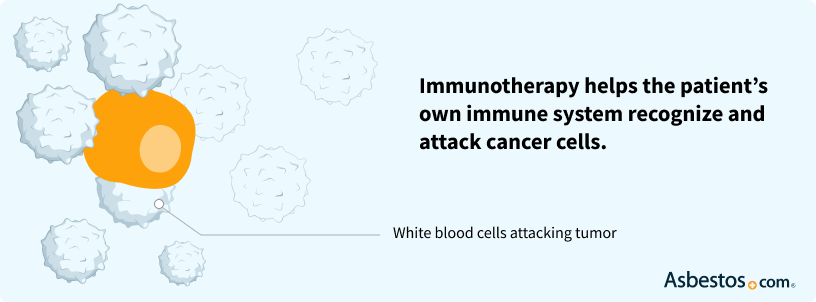
Immunotherapy medications boost your body’s immune system to attack cancer. These medications have demonstrated significant promise for patients.
An immunotherapy vaccine (CRS-207), for example, had a 94% response rate in trial participants. Tumor shrinkage occurred for 85% of participants and 35% saw no new tumor growth.
Commonly Prescribed Mesothelioma Immunotherapy Drugs
Many factors can affect how well someone may respond to immunotherapy drugs. The type of mesothelioma you have can play a key role. Pleural mesothelioma usually has better response rates to immunotherapy compared to peritoneal mesothelioma. A phase I study of SS1P in pleural mesothelioma, for example, found a partial tumor response in 12 of 20 participants.
Mesothelioma cell types can also play an important role. People with the epithelioid type typically respond better to immunotherapy than people with sarcomatoid or biphasic. Your overall health, cancer stage, past treatments and your genetics are also important factors.
The Future of Immunotherapy for Mesothelioma
New immunotherapies are being tested regularly. A recent study found people with mesothelioma can benefit from a treatment that uses 2 immune checkpoint inhibitors to fight cancer.
Clinical trials are also continuing for Imfinzi (durvalumab). The FDA approved this immunotherapy drug in 2017 to treat bladder and lung cancer. Research indicates it can be a second-line treatment for late-stage mesothelioma. It can be used with traditional treatments like surgery or chemo.
A trial in Italy will study patient subgroups. The goal is to find personalized treatments for mesothelioma. They expect to complete the trial before the end of 2026.
Side Effects of Immunotherapy Drugs for Mesothelioma
Common side effects of immunotherapy include coughing, diarrhea, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea and weight loss. Your side effects may increase with a stronger immune response. Immunotherapy drugs usually have milder side effects compared to chemo.
Dr. Estelamari Rodriguez, a thoracic oncologist at the University of Miami Health System, shares with us, “The most common side effects of Opdivo with Yervoy include fatigue, itching, diarrhea, rash, pain in muscles and joints and decreased thyroid hormone. Rarely, inflammation of the lungs (pneumonitis) occurs.”
Common Side Effects of Mesothelioma Chemotherapy Drugs
- Body aches
- Constipation
- Coughing
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- Mouth sores
- Muscle or joint pain
- Nausea
- Skin irritation
- Weight loss
Possible serious side effects include colitis, hepatitis, hormone gland problems, kidney problems and pneumonia. If you experience any of these issues, contact your doctor.
Some drug interactions can also affect how well immunotherapy works. Acetaminophen, antibiotics, corticosteroids, metformin, proton pump inhibitors and steroids may all reduce the potential benefits of immunotherapy. Tell your doctor if you take these medications before starting immunotherapy.
Targeted Therapy Drugs for Mesothelioma
Targeted therapy is a growing area for mesothelioma treatment. It targets specific changes in cancer cells that drive their growth, spread and death. While chemotherapy affects both healthy and cancerous cells, targeted therapy is designed to destroy only cancerous cells.
Common Targeted Therapy Drugs
- Ganetespib: This drug blocks a protein that helps mesothelioma cells grow – heat shock protein 90. It’s still being tested in clinical trials
- NGR-hTNF: It’s currently in phase III trials to test its use in managing recurring mesothelioma. Preliminary data offers hope the drug can become an effective second-line therapy.
- Onconase: This drug is toxic to cancer cells. It showed promise during a phase III trial but failed to improve patient survival enough to receive FDA approval.
- Tazemetostat: This drug targets an enzyme that helps mesothelioma cells grow. It works best in people with a BAP-1 gene mutation, which appears in 60% of mesothelioma cases. The FDA approved it in 2020 to treat epithelioid sarcoma.
Many clinical trials have been the focus of targeted therapy for mesothelioma. One trial in Italy will test 2 proteins. It’ll explore their role in cancer spread and treatment. These proteins, hmgb1 and CXCR4, repair DNA and regulate cell growth and survival. Experts believe targeting the pathways of these proteins may stop tumor growth. They expect to complete the trial in 2027.
Targeted drugs are great for mesothelioma patients. They specifically target the cancer cells and don’t affect normal tissue.
Side Effects of Targeted Therapy Drugs for Mesothelioma
Targeted therapy drugs can cause side effects similar to those of chemo and immunotherapy. Not every person gets every side effect, and some get few or none. Speak to your doctor about any side effects you experience as early as possible.
Common Side Effects of Targeted Therapy Drugs
- Allergic reactions
- Cough
- Fatigue
- High blood pressure
- Nausea
- Skin problems
- Slow wound healing
- Swelling
- Thinning hair
Call your doctor if you have serious side effects, like bleeding or blood clots. Rare autoimmune reactions in the eyes, intestines, liver, lungs, nerves, skin or other organs can be serious or even life-threatening. Heart damage can also occur. This is especially true if targeted therapy is used with certain chemo drugs.
Drug interactions can occur during targeted therapy. You can experience them if you take antibiotics, antivirals, chemo drugs or NSAIDs during treatment. Talk to your doctor about your meds and supplements before targeted therapy.
Anti-Angiogenesis Drugs
Angiogenesis is your body’s way of healing through creating new blood vessels. But, that process can also feeds cancer cells fresh blood, allowing them to grow and spread. Researchers believe anti-angiogenesis drugs might stop mesothelioma and other cancers from spreading.
Common Anti-Angiogenesis Drugs for Mesothelioma
- Avastin (bevacizumab)
- Cediranib
- Cyramza (ramucirumab)
- Nexavar (sorafenib)
- Thalidomide
- Veglin
Studies show that Avastin is the best anti-angiogenesis drug for mesothelioma. No other anti-angiogenesis drug has shown as much promise in trials as Avastin. Combining Avastin with chemo improves overall survival rates according to research.
Side Effects of Anti-Angiogenesis Drugs
Anti-angiogenesis drugs may have milder side effects than some chemo drugs. Common side effects include diarrhea, fatigue, rash and high blood pressure.
Common Side Effects of Anti-Angiogenesis Drugs
Some serious side effects are bowel perforation, blood clots and internal bleeding. They may cause stroke, heart attack or heart failure. Call your doctor if you experience any of these serious side effects.

Photodynamic Therapy Drugs for Mesothelioma
Photodynamic therapy uses drugs to make cancer cells sensitive to light. The light can then destroy them. This is a 2-step treatment. Photofrin, a porfimer sodium, is the only FDA-approved photosensitizer for mesothelioma. It’s also used for other cancers like esophageal cancer.
Researchers are testing photodynamic therapy in pleural mesothelioma patients. They have found it improves survival times. The treatment for peritoneal mesothelioma is still in development. Doctors are looking for a way to deliver light to the abdominal cavity effectively.
Side Effects of Photodynamic Drugs for Mesothelioma
A common side effect of photodynamic therapy is light sensitivity, which lasts for about 6 weeks. Doctors say to avoid sunlight and bright light during this time. Other common side effects are coughing, trouble swallowing, stomach pain and painful or short breaths.
Common Side Effects of Photodynamic Drugs
- Burning
- Coughing
- Painful breathing
- Scarring
- Shortness of breath
- Stomach pain
- Swelling
- Temporary eye or skin sensitivity to light
- Trouble swallowing
PDT may not be suitable for people with large tumors. The light can’t penetrate the entire tumor. Doctors are looking to discover better ways to deliver light to reach deeper tissues and treat larger tumors.
Promising clinical trial results have led some top cancer centers to offer PDT to their patients. The Abramson Cancer Center in Pennsylvania and the Stanford Cancer Institute in California offer PDT for those who qualify. Brigham and Women’s Hospital can also use PDT, but it rarely does for treatment.
Participating in the Future of Mesothelioma Medications
New mesothelioma treatments are constantly evolving. Taking part in a clinical trial is a big part of the process. As a trial participant you’ll be able to try new or emerging mesothelioma treatments.
Clinical trials for mesothelioma usually test new therapies for safety and effectiveness. Some can last for several months or several years. Our Patient Advocates at The Mesothelioma Center can help you find clinical trials. Your doctor can also help you enroll in a trial.
If you qualify, a research coordinator will contact you. Most clinical trials for mesothelioma involve frequent blood and imaging tests. It’s important to weigh any trial risks and benefits. Talking to your family, Patient Advocates and your doctor can help.
- In 2024, the FDA approved the use of Keytruda with chemo drugs for the treatment of mesothelioma in patients who are ineligible for surgery.
- Ongoing clinical trials continue testing immunotherapy and chemotherapy drug combinations to treat mesothelioma.
“This is still being researched and under clinical trials, but hopefully, we can continue to have more novel therapies come out treating mesothelioma. In particular, therapies targeted at patients with BAP1 mutations.”
Common Questions About Mesothelioma Medications
- What questions should I ask my doctor about mesothelioma medications?
-
Questions you might ask your doctor include:
- What side effects can I expect from taking a certain mesothelioma medication?
- Are there things I can do or take that will help counteract any potential side effects?
- Will my other current prescriptions or supplements I take interfere with my mesothelioma medications?
- How long will I need to take these medications?
- How long do mesothelioma medications take to start working?
-
It depends on the medication, type of treatment, stage of the disease and how your body responds to the drug. Cancer cells absorb photodynamic therapy drugs within 24-72 hours.
Chemotherapy drugs can begin affecting cancer cells within days to weeks after your first dose. Anti-angiogenesis drugs can begin blocking new blood vessel formation within days to weeks of starting treatment.
Targeted therapy drugs can start working within weeks to several months. Immunotherapy drugs may take as long as several months.
- Can mesothelioma drugs cure the disease?
-
No, there is no definitive cure for mesothelioma. However, long-term remission is achievable. A combination of treatments such as surgery, chemo and immunotherapy can significantly improve survival and increase the chances of remission.
- Are there alternative or natural therapies to complement mesothelioma drugs?
-
Complementary and alternative mesothelioma treatments may be able to ease symptoms and side effects of treatment. Common alternative therapies include acupuncture, meditation, yoga and medical marijuana. Some other options are herbal medicine and energy therapy.
- What financial assistance is available for mesothelioma medications?
-
The total lifetime costs of mesothelioma care can exceed $150,000. Medicare, Medicaid, private health insurance and VA benefits cover certain treatments. Some drug manufacturers offer patient assistance programs that may offer discounted or free medication for people who are eligible. Seeking financial compensation is another option.
- Will a particular medication disqualify me from other treatments or clinical trials?
-
Yes, certain medications can eliminate you from taking part in a mesothelioma clinical trial. Every trial has specific criteria. Some medications have the potential to interact with other drugs that can compromise the safety or effectiveness of the medication.






