
Dr. Andrea Wolf is the Director of the New York Mesothelioma Program at Mount Sinai in New York City. She focuses on multidisciplinary treatment, clinical research, community outreach and education.
Desmoplastic mesothelioma is a rare cell subtype of sarcomatoid malignant mesothelioma. Asbestos exposure is the primary cause. Symptoms include chest pain and fluid buildup in the lungs. Doctors use biopsies to diagnose desmoplastic mesothelioma.
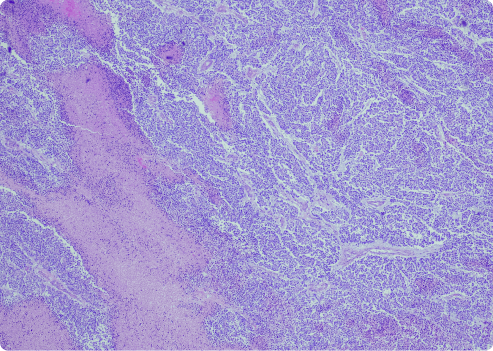
Desmoplastic mesothelioma is a unique type of sarcomatoid mesothelioma. The term “sarcomatoid” describes long, spindle-shaped cells. This subtype is rare. It can be more aggressive than other forms of mesothelioma.
This variant has dense fibrous tissue and fewer cells. Desmoplastic cells are hard to identify. They lack clear patterns. These types of mesothelioma cells form dense nodules of connective tissue in tumors. This can make diagnosis more difficult.
Key Facts About Desmoplastic Mesothelioma
Learn about your diagnosis, top doctors and how to pay for treatment in our free mesothelioma guide.
Get Your GuideUnfortunately, it tends to have a poor outlook and can appear in all types of sarcomatoid mesothelioma. It’s observed in 5% to 10% of all malignant mesothelioma cases.
“Most patients don’t know their cell type when I initially speak with them,” says Dr. Snehal Smart, a Patient Advocate at The Mesothelioma Center. “I help them review their pathology report and explain what sarcomatoid cell types are and what this means for them.”
The main cause of this disease is exposure to asbestos. It can develop in various types of mesothelioma cancer.
Studies show an association between heavy asbestos exposure and sarcomatoid mesothelioma. One study of 180 desmoplastic cases found much higher levels of amosite asbestos fibers in analyzed samples from sarcomatoid tumors.
The most common symptoms include pain, breathing problems and cough. Dense and fibrous areas in the lungs can lead to pulmonary fibrosis that causes shortness of breath.
Common Symptoms of Desmoplastic Mesothelioma
The type of tumor cells doesn’t change the symptoms of mesothelioma. For example, people with pleural mesothelioma often feel short of breath. Abdominal pain may occur in those with peritoneal mesothelioma. If you notice any of these symptoms, consult a health care professional.

Learn about your diagnosis, top doctors and how to pay for treatment in our updated 2025 guide.
Get Your Free GuideA biopsy is the most common method doctors use to diagnose desmoplastic mesothelioma. A biopsy helps determine the cell type and the best treatment options.
Criteria for Diagnosing Desmoplastic Mesothelioma
When desmoplastic mesothelioma spreads, it can seem less aggressive. This makes it easy for doctors to mistake the cells for benign fibrous tissue. Imaging scans, like CT or MRI, can be very helpful for pathologists. It can make it easier to spot the spread of tumors and correctly diagnose tough cases.
The fibrous parts of this type of tumor can sometimes hide variations in the cells. This can block an accurate diagnosis.
Doctors have mistaken desmoplastic pleural mesothelioma for fibrous pleurisy. Other possible misdiagnoses include: Pleural fibrosis, rheumatoid disease or spindle cell sarcoma.
One way to tell desmoplastic mesothelioma apart from sarcomatoid lung cancer is the GATA-3 protein. It’s often present in many mesothelioma cases. But it’s usually absent in lung carcinoma cases. This also helps doctors stage pleural mesothelioma.
Doctors treat desmoplastic mesothelioma with immunotherapy, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. These treatments kill cancer cells, shrink tumors and stop their spread. They ease symptoms, extend life and improve patients’ lives.
One of the most promising first-line treatments is Opdivo with Yervoy. A 2022 study highlighted Opdivo might be particularly effective for sarcomatoid cells. They often have higher levels of a particular protein, PD-L1. This protein makes the cells more receptive to immunotherapy.
Following this, chemo with cisplatin and Alimta is commonly used. Radiation therapy can also be beneficial. It’s especially helpful for reducing painful tumors in the chest wall.
Surgery to remove tumors isn’t usually recommended for this type of mesothelioma. It has a high risk of recurrence within a few months. Some early-stage patients have had better outcomes. Doctors often suggest minor surgeries to drain excess fluid. These include pleurodesis or paracentesis.
The prognosis for mesothelioma with desmoplasia is poor. This cell type tends to spread rapidly. Many patients find their disease is already advanced when they receive a diagnosis.
The sarcomatoid cell type is also the most aggressive and least treatable subtype of mesothelioma. Their shape and behavior make these cells resistant to chemo and radiation. The cancer’s resistance to therapy and its advanced stage at diagnosis limits treatment options. Unfortunately, this can lead to a life expectancy of less than 1 year for those affected.
Genetic and molecular research may offer hope. Emerging therapies, like immunotherapy and targeted treatments, show promise in clinical trials.
Survival rates range from 4 to 12 months after diagnosis. Studies have reported a median survival of 3.8 months with 1 patient living 11.5 months.
A historic 7-year study looked at 255 patients with mesothelioma from 1982 to 1989. Researchers found 17 cases of the desmoplastic subtype. Among these, 11 were pure sarcomatoid and 6 were biphasic. The biphasic type has both sarcomatoid and epithelial cells. The average survival time was about 5.8 months for the pure sarcomatoid variant and 6.8 months for the biphasic variant.
These statistics can feel overwhelming. It’s important to seek support and explore treatment options. Every patient’s journey is unique. There are resources available to help navigate this difficult time.
Asbestos exposure is the primary cause of desmoplastic mesothelioma. Though not every patient with the disease has a known history of exposure.
Support includes counseling, financial aid and transportation. There are also resources offering help around the house. Families can access support resources a number of ways. These include: Support groups, social workers, therapists, cancer centers and non-profit organizations.
No alternative therapy has proven successful for any type of mesothelioma. Some patients do report complementary therapies help them manage their symptoms. Immunotherapy drugs, however, are helping people with desmoplastic mesothelioma live longer.
Yes, desmoplastic mesothelioma has the potential to spread to other parts of the body. All cell types of mesothelioma tend to spread locally before traveling far from their origin. Sarcomatoid cell types tend to spread quicker than epithelioid cells.
Stay up-to-date on treatment, research, clinical trials, doctors and survivors
The information on this website is proprietary and protected. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Any unauthorized or illegal use, copying or dissemination will be prosecuted. Please read our privacy policy and terms of service for more information about our website.
This website and its content may be deemed attorney advertising. Prior results do not predict a similar outcome.
The Mesothelioma Center’s claim as the most trusted resource is based on our more than 150 5-star Google and BBB reviews. Our organization also helps more than half of all mesothelioma patients annually diagnosed.
Your web browser is no longer supported by Microsoft. Update your browser for more security, speed and compatibility.
If you are looking for mesothelioma support, please contact our Patient Advocates at (855) 404-4592
The Mesothelioma Center at Asbestos.com has provided patients and their loved ones the most updated and reliable information on mesothelioma and asbestos exposure since 2006.
Our team of Patient Advocates includes a medical doctor, a registered nurse, health services administrators, veterans, VA-accredited Claims Agents, an oncology patient navigator and hospice care expert. Their combined expertise means we help any mesothelioma patient or loved one through every step of their cancer journey.
More than 30 contributors, including mesothelioma doctors, survivors, health care professionals and other experts, have peer-reviewed our website and written unique research-driven articles to ensure you get the highest-quality medical and health information.
My family has only the highest compliment for the assistance and support that we received from The Mesothelioma Center. This is a staff of compassionate and knowledgeable individuals who respect what your family is experiencing and who go the extra mile to make an unfortunate diagnosis less stressful. Information and assistance were provided by The Mesothelioma Center at no cost to our family.LashawnMesothelioma patient’s daughter


Selby, K. (2025, July 31). Desmoplastic Mesothelioma. Asbestos.com. Retrieved December 18, 2025, from https://www.asbestos.com/mesothelioma/desmoplastic/
Selby, Karen. "Desmoplastic Mesothelioma." Asbestos.com, 31 Jul 2025, https://www.asbestos.com/mesothelioma/desmoplastic/.
Selby, Karen. "Desmoplastic Mesothelioma." Asbestos.com. Last modified July 31, 2025. https://www.asbestos.com/mesothelioma/desmoplastic/.

Dr. Andrea Wolf is the Director of the New York Mesothelioma Program at Mount Sinai in New York City. She focuses on multidisciplinary treatment, clinical research, community outreach and education.
Our fact-checking process begins with a thorough review of all sources to ensure they are high quality. Then we cross-check the facts with original medical or scientific reports published by those sources, or we validate the facts with reputable news organizations, medical and scientific experts and other health experts. Each page includes all sources for full transparency.
Please read our editorial guidelines to learn more about our content creation and review process.
