Mesothelium
The mesothelium is a slippery, protective membrane of flattened mesothelial cells that line the lungs, abdomen, heart and testes. Mesothelioma cancer can develop in the mesothelium because of asbestos exposure.
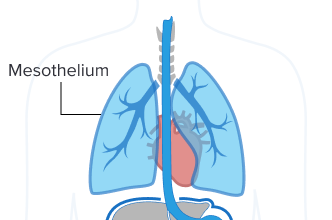
What Is the Mesothelium?
The mesothelium is a thin membrane composed of specialized cells, known as mesothelial cells, that protect organs. This layer helps the body respond to injuries and diseases. It also moves serosal fluid across cavities and manages inflammation. Doctors identify these membranes by the organs they cover.
Mesothelium Identified by Location
- The pleural mesothelium covers the lungs and chest wall.
- The peritoneal mesothelium covers the abdominal organs and abdominal wall.
- The pericardial mesothelium covers the heart.
- The tunica vaginalis covers the testes.
Inhaled asbestos fibers can get trapped in the mesothelium. They cause irritation and harm to the soft tissue over time. The lymphatic system may carry the fibers into the mesothelial layers. Asbestos causes malignant mesothelioma, lung cancer, asbestosis and other diseases.
Mesothelium Structure and Function
The mesothelium has two layers: Visceral and parietal. The visceral mesothelium covers the internal organs. The parietal mesothelium covers the serosal cavity.
Serosal fluid helps the layers move smoothly against each other. While the mesothelium’s role is protection, its tissue is slow to renew. Less than 1% of the cells undergo cell division at any one time.
Functions of the Mesothelium
- Blood clotting to heal wounds
- Inflammation and tissue repair
- Presenting immune proteins to lymphocytes (immune cells)
- Protection against invading microorganisms
- Transporting fluids and cells
- Tumor cell adhesion to prevent cancerous spreading
Research on immune and mesothelial cells has improved over the last decade. Immunotherapy studies, which may improve mesothelioma treatment, reveal the interactions between these two types of cells.
Diseases of the Mesothelium
Cancer can start in the mesothelium from inflammation and scarring. If this damage does not heal, the mesothelium may form fibrous adhesions. These changes can cause mesothelioma and other cancers.
Benign conditions also develop in the mesothelium. For example, mesothelial hyperplasia is a benign disease. But it may resemble cancer. Effusions are benign but may contain cancer cells if cancer is present. Effusions occur when fluid builds up between the layers of the mesothelium. A pleural effusion accumulates around the lungs. While a peritoneal effusion accumulates around the abdomen.
Mesothelioma survivor Jayda K.’s effusion aided her diagnosis. “As a young woman with abdominal pain, I had a really hard time convincing someone I was in pain. A really hard time. I was told it was just my period,” Jayda said. Doctors removed more than a gallon of fluid and saw tumors on her peritoneum. A biopsy confirmed her peritoneal mesothelioma diagnosis.
Pleural Diseases
Benign and cancerous diseases of the pleura can develop because of asbestos exposure. Pleural mesothelioma is the most serious pleural disease.
Types of Pleural Diseases
- Atelectasis is a contraction of pleural scar tissue that folds the pleura into the lung. This folding action causes the lungs to underinflate.
- Pleural plaques are fibrous scar tissue on the pleura that may become calcified.
- Pleural thickening is extensive scarring that thickens and restricts the pleura.
- Pleural mesothelioma is a cancer of the pleura.
- Pleuritis is inflammation of the pleura.
Its latency period is between 20 and 60 years. If you develop other pleural diseases, it is important to see a doctor early. An earlier diagnosis may improve treatment outcomes.
Peritoneal Diseases
Benign and cancerous diseases can also develop in the peritoneum. Asbestos exposure is the main cause of peritoneal mesothelioma.
Types of Peritoneal Diseases
- Intra-abdominal adhesions are wounds in the peritoneum.
- Peritoneal mesothelioma is a cancer of the peritoneum.
- Peritonitis is inflammation of the peritoneum.
- Primary peritoneal serous carcinoma is another cancer of the peritoneum.
- Ultrafiltration failure of the peritoneum leads to fluid buildup.
Peritonitis is when the peritoneum becomes inflamed. Bacterial or fungal infections often cause peritonitis.
A cancer called primary peritoneal serous carcinoma can develop in the peritoneum. A 2022 study published in the Scholars Journal of Medical Case Reports compared it to advanced-stage serous ovarian carcinoma, highlighting its importance in understanding these conditions.
Pericardial Diseases
Several benign conditions and cancers can develop in the pericardium. Pericardial mesothelioma is the most serious of the pericardial diseases, but it’s also rare.
Types of Pericardial Diseases
- Cardiac tamponade is compression of the heart by fluid accumulation.
- Pericardial constriction is scarring and a loss of elasticity of the pericardium.
- Pericardial mesothelioma is a cancer of the pericardium.
- Pericarditis is inflammation of the pericardium.
- Several other cancers can develop in the pericardium, including sarcomas, lymphoma and primitive neuroectodermal tumors.
About 1% of people diagnosed with mesothelioma have the pericardial type. Its treatment options are limited because of the sensitive location of the tumors.
Tunica Vaginalis Diseases
Benign and cancerous diseases can develop in the tunica vaginalis. Testicular mesothelioma is the most common asbestos-related disease of the tunica vaginalis.
Types of Diseases of the Tunica Vaginalis
- Benign tumors can develop, including adenomatoid tumors, scrotal tunica cysts, lipoma and leiomyoma.
- Fibrous pseudotumors are benign lesions of the tunica vaginalis.
- Hydrocele is an abnormal amount of fluid between the layers of the tunica vaginalis.
- Mesenchymal malignant tumors, lymphomas and serous borderline malignant tumors can develop in the tunica vaginalis.
- Scrotal calculi are calcified deposits that form between the layers of the tunica vaginalis.
- Testicular mesothelioma is cancer of the tunica vaginalis.
If you were exposed to asbestos and have unusual symptoms in your lungs, abdomen, heart or testes, please see your doctor. It’s always best to stay proactive about your health.
Mesothelium and Asbestos Exposure
Asbestos fibers can travel to the mesothelium once inhaled. Over time, these fibers cause irritation, scarring and DNA damage. These factors leads to diseases of the mesothelium such as mesothelioma.
Scientists have studied how asbestos reaches the mesothelium. A 2023 study in the scientific journal PNAS shows the lymphatic system plays a role. This system helps remove waste and fight infections. Some asbestos fibers travel through lymphatic transport to the mesothelium. This increases mesothelioma risk because the fibers may stay in the body, causing long-term damage.
To lower the risk, people should avoid asbestos exposure. Follow safety rules when working in old buildings and learn products to watch out for.

How Are Diseases of the Mesothelium Treated?
Doctors treat mesothelial diseases in several ways. The course of treatment depends on the diagnosis and the location of the mesothelium. Cancer of the mesothelium may involve multimodal therapy. Benign conditions do not require aggressive treatment.
Treatments for Diseases of the Mesothelium
- Chemotherapy uses strong medicine to kill cancer cells in the mesothelium.
- Immunotherapy can shrink tumors in the mesothelium.
- Minimally invasive surgery drains extra fluids to improve symptoms.
- Radiation can shrink tumors and relieve pain in chest wall tumors.
- Surgery can remove mesothelial tumors to slow disease.
Each patient’s treatment plan depends on their health and the type of disease. Doctors can help people manage mesothelial diseases and improve their quality of life with the right care.
Recommended Reading


