Get Your Free Mesothelioma Guide

Find a Top Mesothelioma Doctor

Access Help Paying for Treatment

Ovarian cancer refers to any malignant tumor that begins in the ovaries. Exposure to asbestos is strongly associated with an increased risk of ovarian cancer. Ovarian cancer is the fifth-most common cause of cancer-related deaths among women older than 35.
Ovarian cancer is a disease that involves the abnormal growth of cells in the ovaries. It can develop in one or both ovaries, as well as the fallopian tubes. Epithelial ovarian carcinoma — which develops on the outer surface of the ovary — is the most common form, accounting for 85 to 90% of cases.
Approximately 19,880 women were diagnosed with ovarian cancer in 2022. Women have a 1 in 75 chance of developing the illness during their lifetime. The five-year survival rate is 47.6%. Treatment for ovarian cancer is very effective when the cancer is caught at an early stage.
Quick Facts About Ovarian Cancer
Risk factors include a family history of cancer, age, never having been pregnant, the use of certain hormone therapies and weight. Regularly taking birth control pills may reduce risk.
The International Agency for Research on Cancer lists asbestos exposure as a known cause of ovarian cancer. The agency’s 2012 review documented numerous research studies linking ovarian cancer to the accumulation of asbestos fibers in ovarian tissue.
Get Your Free Mesothelioma Guide

Find a Top Mesothelioma Doctor

Access Help Paying for Treatment

Once asbestos fibers enter the body, they can become lodged in soft tissues permanently, causing inflammation and cellular damage over the course of many years. Researchers have different theories about how asbestos fibers accumulate in ovarian tissue.
Recent studies have linked asbestos exposure to an increased risk of ovarian cancer, particularly among women who may have used asbestos-contaminated talcum powder. Asbestos and talc are naturally occurring minerals that are often found near each other. Talc can become contaminated with asbestos during the mining process.
Microscopic asbestos fibers cannot be seen, smelled or tasted, and asbestos exposure causes no immediate symptoms. Manufacturers frequently added asbestos to consumer products and building materials from the late 1800s until the 1980s. Some products, such as roofing materials, are still made with asbestos.
Women who worked in occupations associated with asbestos exposure have higher rates of ovarian cancer. The wives and daughters of asbestos-exposed workers also have a higher risk because of exposure to asbestos on the workers’ skin, hair and clothes.
Inhaling or swallowing asbestos dust at a worksite causes most asbestos-related diseases. Ingested or inhaled asbestos fibers may have traveled to the ovaries through the bloodstream or lymphatic system.
Asbestos-contaminated talcum powder products have caused cancer in people who inhaled the powder on a regular basis. Some researchers suggest when women applied contaminated talcum powder to their genitals after showering or bathing, asbestos fibers may have also traveled up the reproductive tract to their ovaries.
A 2021 retrospective research study concluded that ovarian tumors can be associated with asbestos or contaminated talc exposure. The researchers examined ovarian tissue samples, scanning electron microscopy and detected asbestos fibers with talc crystals in multiple cases.
Ovarian cancer often does not cause major symptoms until it has grown and spread throughout the pelvis and abdomen.
Common symptoms include:
Other symptoms may include:
Many conditions besides cancer can cause these symptoms, so the key is to watch out for symptoms that are persistent and unusual. If a woman experiences any of these potential signs of ovarian cancer more often or more intensely than normal, she should make an appointment with a gynecologist.
The process of diagnosing ovarian cancer typically begins with a gynecologist physically examining the pelvis. An imaging scan such as an ultrasound, CT scan, MRI or PET scan is then ordered. The diagnostic process is complex, because ovarian cancer can appear similar to other types of cancer such as peritoneal mesothelioma, which asbestos also causes.
If there is a buildup of fluid in the abdomen — a condition called ascites — doctors may drain the buildup through a hollow needle and then examine the fluid for cancer cells. A blood test for the CA 125 protein can also point to the presence of ovarian cancer.
A surgeon can then conduct a laparoscopy to examine the inside of the pelvis with a tiny camera probe. This allows the medical team to see the extent of the cancer growth before going ahead with more invasive tumor-removing surgery.
Doctors usually treat ovarian cancer with a combination of surgery and chemotherapy. However, an individual patient’s treatment plan and prognosis depends heavily on the cancer’s stage or how far the cancer has spread.
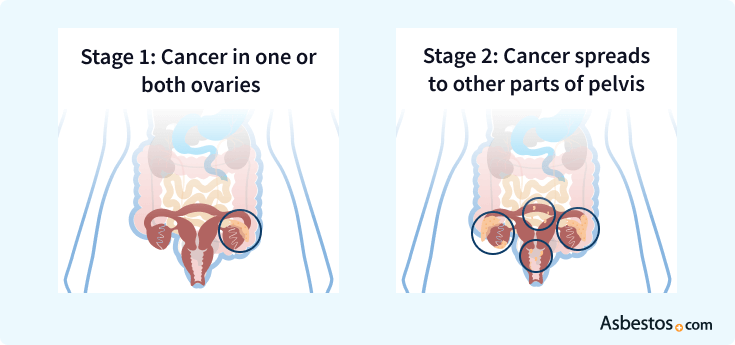
5-year survival rate: 90%
Currently, fewer than 20% of cases are diagnosed while the cancer is still localized to a single ovary. These fortunate patients sometimes have the option to have only one ovary and fallopian tube surgically removed, leaving their uterus and the other ovary intact so they can still have children. Depending on the specific cell type of the cancer, some stage 1 patients also may not need chemotherapy.
5-year survival rate: 70%
Ovarian cancer surgery usually involves removing the uterus and both ovaries and fallopian tubes, which will prevent the patient from ever becoming pregnant and cause her to go into menopause if she has not done so already. After surgery, the medical team usually administers three to six cycles of a chemotherapy drug combination such as carboplatin and paclitaxel.
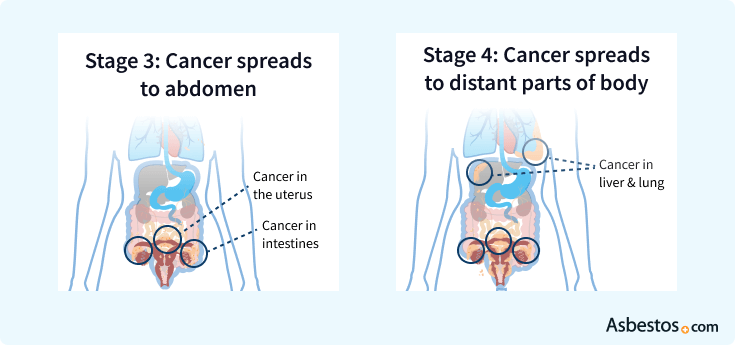
5-year survival rate: 39%
If the cancer has spread into the abdomen, the surgeon may have to remove parts of the colon, bladder, stomach, liver, pancreas, spleen and gallbladder in addition to the reproductive organs.
5-year survival rate: 17%
If the cancer has spread to distant organs in the patient’s body, the medical team may recommend surgery to remove as much tumor growth as possible. They may also advise the patient to only undergo chemotherapy to slow the growth of the cancer.
Recommended ReadingYour web browser is no longer supported by Microsoft. Update your browser for more security, speed and compatibility.
If you are looking for mesothelioma support, please contact our Patient Advocates at (855) 404-4592
The Mesothelioma Center at Asbestos.com has provided patients and their loved ones the most updated and reliable information on mesothelioma and asbestos exposure since 2006.
Our team of Patient Advocates includes a medical doctor, a registered nurse, health services administrators, veterans, VA-accredited Claims Agents, an oncology patient navigator and hospice care expert. Their combined expertise means we help any mesothelioma patient or loved one through every step of their cancer journey.
More than 30 contributors, including mesothelioma doctors, survivors, health care professionals and other experts, have peer-reviewed our website and written unique research-driven articles to ensure you get the highest-quality medical and health information.
My family has only the highest compliment for the assistance and support that we received from The Mesothelioma Center. This is a staff of compassionate and knowledgeable individuals who respect what your family is experiencing and who go the extra mile to make an unfortunate diagnosis less stressful. Information and assistance were provided by The Mesothelioma Center at no cost to our family.LashawnMesothelioma patient’s daughter


Dixon, S. (2024, June 27). Ovarian Cancer. Asbestos.com. Retrieved August 5, 2025, from https://www.asbestos.com/cancer/ovarian/
Dixon, Suzanne. "Ovarian Cancer." Asbestos.com, 27 Jun 2024, https://www.asbestos.com/cancer/ovarian/.
Dixon, Suzanne. "Ovarian Cancer." Asbestos.com. Last modified June 27, 2024. https://www.asbestos.com/cancer/ovarian/.
Dr. Andrea Wolf is the Director of the New York Mesothelioma Program at Mount Sinai in New York City. She focuses on multidisciplinary treatment, clinical research, community outreach and education.
Our fact-checking process begins with a thorough review of all sources to ensure they are high quality. Then we cross-check the facts with original medical or scientific reports published by those sources, or we validate the facts with reputable news organizations, medical and scientific experts and other health experts. Each page includes all sources for full transparency.
Please read our editorial guidelines to learn more about our content creation and review process.
