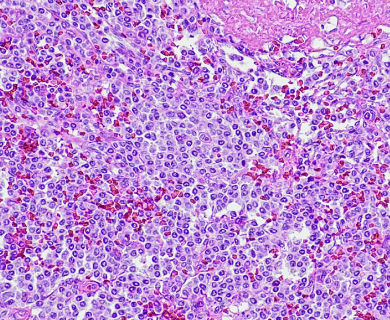
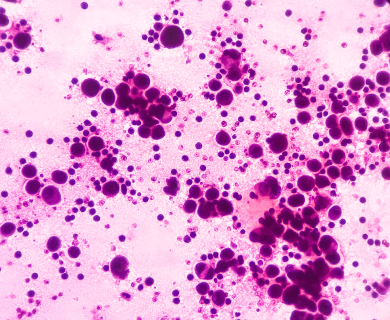
Christine S. was diagnosed with epithelial malignant mesothelioma on October 11, 2007. She had multiple rounds of chemotherapy. Six of them used Alimta. It helped shrink her cancer. She stressed the benefits of medical advice and accepted her diagnosis.
Epithelioid Mesothelioma
Epithelioid mesothelioma is a rare cancer caused by asbestos exposure. It accounts for 50% to 70% of all cases. It develops in the lining of the lungs, abdomen or heart. Epithelioid cells respond better to treatment than other mesothelioma cell types. Life expectancy ranges from 14.4 months to 51.5 months.
What Is Epithelial Mesothelioma?
Epithelial mesothelioma is a type of cancer composed of epithelioid cells. It occurs when epithelial cells in the mesothelium turn cancerous and form tumors. The mesothelium is the protective tissue that lines the lungs, abdomen, heart and testes. Exposure to asbestos fibers is the primary cause of epithelioid mesothelioma.
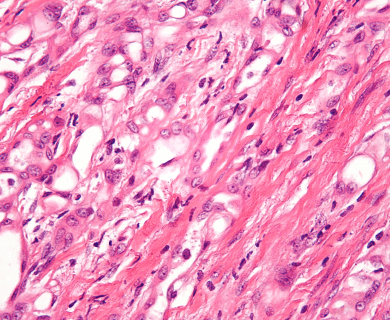
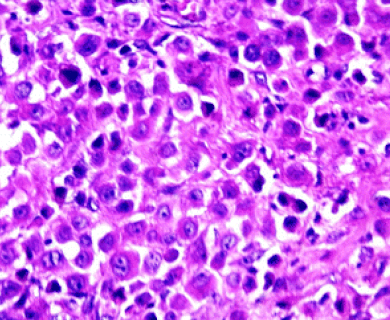
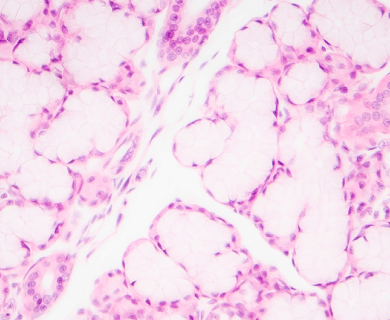
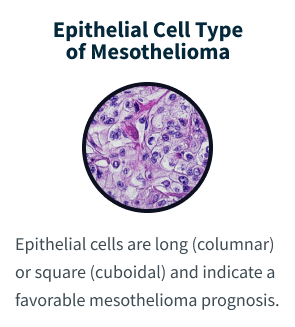
Epithelial mesothelioma, or epithelioid mesothelioma, is the most common mesothelioma cell type. It can develop in the lining of the lungs (pleural), abdomen (peritoneal), heart (pericardial) or testes (testicular). Epithelial cells are long (columnar) or square (cuboidal). They indicate a favorable mesothelioma prognosis.
Patients with the epithelial mesothelioma live an average of 18 months; a life expectancy that’s much longer than those with biphasic or sarcomatoid cell types. Epithelial cells respond better than others to aggressive treatment.
- About 54% of pleural mesothelioma tumors contain epithelial cells.
- Doctors diagnose 1,500 to 2,100 epithelioid mesothelioma patients annually.
- Epithelial mesothelioma accounts for 50% to 70% of all cases.
- Epithelioid cells comprise about 75% of peritoneal mesothelioma tumors.
- The epithelioid type has the best prognosis of all types of mesothelioma.
What Causes Epithelial Mesothelioma?
The primary risk factor and cause of epithelioid mesothelioma is the same as other cell types of mesothelioma: Asbestos exposure. Inhalation or ingestion of asbestos fibers causes tissue inflammation and DNA damage, leading to cancer development decades later.
Asbestos fibers cause inflammation in the mesothelium. This protective internal lining is composed of tissue called epithelium because it’s made of epithelial cells.
Most people diagnosed with epithelioid mesothelioma worked with asbestos products long before their diagnosis. All mesothelioma cell types have a latency period of 20 to 60 years. The first symptoms may not show up for decades after the initial asbestos exposure.
Epithelioid Mesothelioma Symptoms
Epithelioid mesothelioma symptoms often include cough, shortness of breath and lack of appetite. As the disease progresses, more severe symptoms may appear. Many symptoms depend on tumor location and size.
- Abdominal pain or bloating
- Bowel or bladder changes
- Chest tightness or pain
- Cough, hoarseness or difficulty swallowing
- Difficulty breathing
- Fatigue
- Fever or night sweats
- Fluid buildup in the chest or abdomen (effusion)
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea, vomiting or diarrhea
- Unexplained weight loss
Mesothelioma cancer symptoms are the same, no matter the cell type. Patients with different cell types experience the same symptoms. But the cell type affects which treatments are most helpful. Talk to your doctor if you experience any of these symptoms.
Access top doctors, and get help scheduling appointments.
Connect NowDr. Jacques Fontaine, Pleural Mesothelioma Specialist

How Is Epithelioid Mesothelioma Diagnosed?
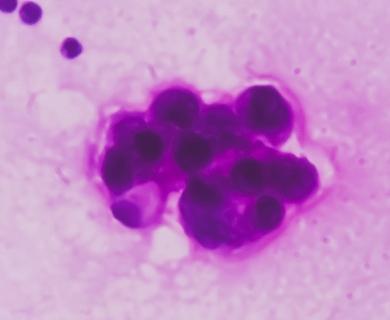
A tissue biopsy is the only way to diagnose epithelial mesothelioma. This procedure samples suspicious tissue to confirm the cell type under a microscope. Epithelial mesothelioma cells clump together in groups and don’t tend to travel. These cell types are less likely to spread to other areas of the body.
“Epithelial subtype mesothelioma describes the type of cells the pathologist is seeing under the microscope when they look at a patient’s tumor,” mesothelioma specialist Dr. Andrea Wolf of Mount Sinai Hospital told The Mesothelioma Center at Asbestos.com.
- Diagnosing epithelioid mesothelioma requires a biopsy.
- Imaging scans can show abnormalities, but they alone cannot diagnose cancer.
- Blood tests aren’t helpful for diagnosis, but research is ongoing to make them more effective.
Epithelial mesothelioma cells can take on a variety of shapes and sizes. These include cuboid (square), columnar (long) or squamous (flat). The cells also carry DNA within a visible nucleus.
The Patient Advocates at The Mesothelioma Center say many newly diagnosed patients who call to ask questions about their mesothelioma diagnosis typically don’t know their cell type. It’s important to ask your doctor about cell type because it will help you understand your symptoms, treatment and prognosis.
Understanding Your Pathology Report
After a biopsy, the pathologist will create a report for your physician. The pathology report describes the types of mesothelioma cells found in a patient’s tumors and a final diagnosis.
The specimen description section of your pathology report will include which cell type was found. The cell type informs your doctor how your cancer might progress. It also determines which treatment options may be best for you.
When I first speak with a patient, I ask about their diagnosis and cell type. If they say they don’t know, I explain how to find it on their pathology report. I also explain the three cell types and their meaning for their mesothelioma journey.
Patient Advocates can help people with mesothelioma understand their pathology report. They can walk you through each section and explain what the information means about your diagnosis and potential treatment options.
Diagnosing Epithelial Mesothelioma With Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry is a technique for studying cancer tissues. Pathologists use tests to identify certain proteins associated with epithelial cells. If pathologists identify proteins found in other cancers instead, they’ll rule out epithelioid mesothelioma.
The proteins that help doctors identify epithelioid mesothelioma from different types of cancer include: Calretinin, D2-40, keratin 5/6, podoplanin and WT-1 protein. An official diagnosis relies on more than immunohistochemistry, however, including the tumor’s appearance, location and other types of cell characteristics.
Epithelial Cell Subtypes
Pathologists can identify epithelioid cell subtypes with immunohistochemistry. If you have a specific subtype, it could influence your treatment options or mesothelioma prognosis. Rare subtypes could lead to a misdiagnosis. Some epithelioid cell subtypes, such as adenomatoid, are associated with a better mesothelioma survival rate.
“When I speak with a patient who is hesitant to have a biopsy, which is rare, I explain that knowing the cell type is imperative when assessing treatment options,” Danielle said.
Talk to your mesothelioma doctor about your cell type, cancer stage and speed of tumor growth (tumor grade). Ask how these factors affect your treatment plan and prognosis.
How Is Epithelioid Mesothelioma Treated?
Doctors often treat epithelioid mesothelioma with a combination of treatments, which is referred to as multimodal therapy. Early-stage cases typically get aggressive treatment with surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Late-stage cases respond better to palliative care with immunotherapy, chemotherapy and Tumor Treating Fields therapy.
“The epithelial type does tend to be more favorable,” explains Dr. Wolf. “It does tend to respond to chemotherapy a little more easily.”
- Chemotherapy can triple the mesothelioma survival rate.
- Immunotherapy can extend survival to 18 months for many patients.
- Radiation therapy helps manage symptoms and prevent local recurrence.
- Surgery extends survival an average of 2 years or 5 years after HIPEC.
Your mesothelioma treatment will depend on the cancer stage, tumor extent and overall health. Of the 3 cell types, epithelial mesothelioma responds best to treatment.
Consider a second opinion at a top cancer center. The specialists at these centers have the experience to diagnose and treat epithelioid mesothelioma effectively. They can offer clinical trials and multidisciplinary treatment to control the disease with different therapies.
Epithelial Mesothelioma Prognosis
The epithelioid mesothelioma prognosis is better than the outlook for biphasic and sarcomatoid cells. Epithelioid cells respond the best to treatment and don’t spread as quickly as the other cell types, which translates into longer survival.
The 5-year survival rate for epithelioid pleural mesothelioma is 12%. A peritoneal mesothelioma study showed a median survival of 55 months for patients with epithelioid cells whereas patients with sarcomatoid or biphasic cells had a median survival of 7 to 13 months.
The survival rate for epithelial patients is overall significantly longer. Epithelial cell type is the best mesothelioma cell type to have. This patient will have more options, such as surgery, and is more likely to respond to treatment.
Epithelioid patients live 200 days longer on average than patients with other cell types. The average life expectancy of epithelial malignant mesothelioma patients is 18 months. The overall survival of all cell types drops when the disease metastasizes or spreads.
Common Questions About Epithelioid Mesothelioma
- Where can I get treatment for epithelial cell mesothelioma?
-
Look for mesothelioma specialists with years of experience treating pleural and peritoneal mesothelioma. Oncologists need training to treat epithelioid mesothelioma. Our Patient Advocates can help you find a top doctor who treats epithelial mesothelioma.
- Can epithelioid mesothelioma be prevented?
-
Asbestos exposure is the primary cause of mesothelioma. Avoiding it is the best way to prevent mesothelioma. If you have a history of asbestos exposure, talk to your doctor about cancer screenings, which may aid in an early diagnosis.
- Is epithelioid mesothelioma curable?
-
Unfortunately, epithelioid mesothelioma has no cure. But patients with the epithelioid cell type have the most treatment options. This cell type responds the best to all forms of treatment.
- Is there any ongoing research on epithelioid mesothelioma?
-
Researchers are constantly looking for mesothelioma patients with the epithelioid cell type for clinical trials. They seek out these participants because epithelioid is the disease’s most common cell type. Studying epithelioid patients lets researchers learn how a drug or therapy will affect most patients diagnosed with mesothelioma.
- How can epithelial cells turn into mesothelioma?
-
Long-term inflammation can lead to mutations in epithelial cells, eventually giving rise to cancer. When you inhale asbestos fibers, they can become trapped in the lung lining and cause inflammation. Asbestos causes cancerous mutations in epithelial cells over time, leading to mesothelioma tumors decades after the initial exposure.