When Wally Rogers’ tumors grew after rounds of chemo, a specialist recommended Keytruda. The immunotherapy drug had an almost immediate effect. CT scans showed no sign of sarcomatoid mesothelioma after 8 months on Keytruda.
Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma
Sarcomatoid malignant mesothelioma is a rare asbestos-related cancer that primarily develops in the lining of the lungs. The sarcomatoid cells that make up these mesothelioma tumors are resistant to treatment, but evidence shows the condition responds best to immunotherapy.
What Is Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma?
Sarcomatoid mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive asbestos-related cancer. The cancer forms when sarcomatoid cells grow into tumors. These cells are long and shaped like spindles. Tumors can develop in the lining of the lungs, abdomen, heart or testes.
Key Facts About Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma
- Sarcomatoid mesothelioma, or spindle cell mesothelioma, makes up 10% to 20% of all cases.
- The fibrous nature of sarcomatoid cells makes them resistant to treatment. This makes for a poor outlook (prognosis).
- Advances in immunotherapy have demonstrated double survival rates for some sarcomatoid mesothelioma patients.
Sarcomatoid cells grow in connective tissues, such as bones, nerves and tendons. The sarcomatoid type is the rarest of the 3 primary cell types of mesothelioma. For comparison, about 60% of patients have the epithelial type, and 20% have the biphasic type.
Sarcomatoid tumors spread easily and are tough to treat. This leads to a worse outlook for this type of mesothelioma. However, new immunotherapy treatments have helped some patients beat the odds.
What Causes Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma?
Asbestos is the main cause of sarcomatoid mesothelioma. When people breathe in asbestos fibers, these fibers build up in the body. This buildup causes irritation and inflammation. Over time, this can cause mutations that turn mesothelial cells into cancer cells.
Mesothelioma risk factors include asbestos exposure at work, in the military and from the environment. Mainly, industrial workers faced exposure. Veterans were at risk in shipyards and military bases. People were also unknowingly exposed when someone in their home took home asbestos fibers on their work clothes or body.
Sarcomatoid mesothelioma survivor Gene Hartline worked as a sheet metal contractor, where he believes he was exposed to asbestos. He tells us, “The diagnosis was tough, especially when they said 4-6 months to live. But now, with this immunotherapy, I’m not going downhill anymore. I’m on the climb back up. And that feels good.”
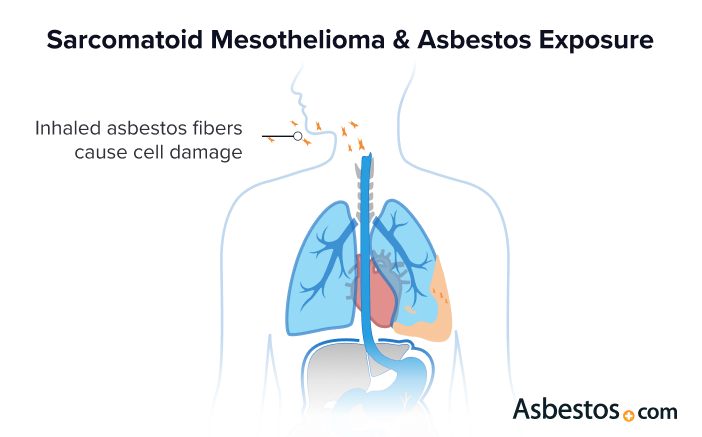
Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma Symptoms
Sarcomatoid mesothelioma has symptoms of shortness of breath, chest pain and coughing. Severe cases can lead to breathing difficulties and a lasting cough. Symptoms may take 20 to 60 years to develop.
Symptoms depend on tumor location. Sarcomatoid cells are mainly in the lung lining. But in sarcomatoid peritoneal cancer, symptoms are different. Patients may face bowel issues, pain and swelling in the abdomen.
Symptoms of Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma
- Anemia (low iron)
- Chest pain or abdominal fullness
- Coughing up blood
- Fatigue and extreme tiredness
- Lack of appetite, anorexia and nausea
- Low blood oxygen levels
- Persistent cough
- Prolonged hoarseness
- Shortness of breath
- Weight loss and weakness
A 2023 review published in the journal Thoracic Cancer found sarcomatoid mesothelioma symptoms are often vague. This makes early diagnosis tough, as patients might not mention key symptoms. These symptoms are often like those of common illnesses, such as bronchitis.
If you have any mesothelioma signs or a history of asbestos exposure, speak with a specialist as soon as possible. If you have a history of asbestos exposure, speak with your doctor about early screening. An early diagnosis may mean more treatment options.

How Is Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma Diagnosed?
When patients go to the doctor with mesothelioma symptoms, doctors order imaging tests such as X-rays or CT scans. If X-rays reveal abnormalities, they’ll collect a tissue sample for a biopsy. Another doctor reviews the sample under a microscope and creates a pathology report.
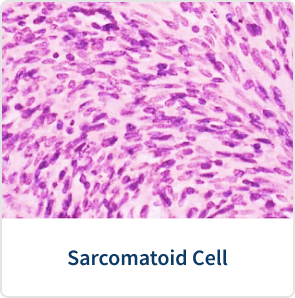
Doctors diagnose sarcomatoid mesothelioma through biopsies. A biopsy is the only test that reveals specific details, such as cell type.
Pathology stains are tests that make cell features visible under a microscope. Sarcomatoid cells are long, narrow and shaped like spindles.
Doctors diagnose 300 to 600 new patients with this cell type yearly. About 98% of these patients have pleural mesothelioma and about 2% have peritoneal mesothelioma.
Understanding Your Pathology Report
Your pathology report describes the tumor cell type, biomarkers and cancer stage. Your doctor uses the findings to complete your diagnosis. Ask your doctor about your report and how it affects your treatment options.
“Most patients don’t know their cell type when I initially speak with them,” said Dr. Snehal Smart, a medical doctor and Patient Advocate at The Mesothelioma Center. “I help them review their pathology report and explain what sarcomatoid cell types are and what this means for them.”
Patient Advocates can walk you through each section of the report to make sure you have a good understanding of what it says. They can answer questions about how a diagnosis may impact treatment and prognosis. Immunohistochemical markers, or biomarkers, can not only help diagnose you, but they can also help your doctor pick the best medication for you. For example, if sarcomatoid cells in your tumor show high PD-L1 levels (seen after staining), your doctor will likely recommend checkpoint inhibitors like Opdivo and Yervoy.
“Sarcomatoid mesothelioma is a rare subtype in contrast to epithelial. Sarcomatoid tends to be a little more locally progressive.”
Rare Sarcomatoid Cell Types
Rare sarcomatoid mesothelioma cell subtypes can provide information about your prognosis. These types come in 3 categories. Some may provide a better prognosis. Others can point to a higher chance of metastasis.
Rare Sarcomatoid Cells
- Desmoplastic mesothelioma: This sarcomatoid subtype is one of the most difficult to diagnose. With this cell type, doctors may be unable to track if your tumor is growing.
- Lymphohistiocytoid mesothelioma: These tumors contain inflammatory and immune cells. This can translate to more symptoms but also a better life expectancy.
- Transitional mesothelioma: This type grows and spreads like other subtypes. It consists of large, spindle-shaped cells that make the disease easier to diagnose.
These sarcomatoid mesothelioma subtypes are generally rare. They most often develop in the pleura of the lungs. Ask your physician whether there are any abnormalities in your pathology report. They can offer more information on your outlook (prognosis).
What Is the Survival Rate of Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma?
A recent study showed the median survival for sarcomatoid mesothelioma was 15 months with immunotherapy and 10.7 months with chemotherapy. Each person’s outlook or prognosis differs based on health, tumor location and metastasis.
The life expectancy for sarcomatoid pleural mesothelioma cases is about 5 months. For peritoneal cases, the average is 10 to 11 months. Women with the sarcomatoid type often outlive men.
The shape of these cells makes them less likely to stick together. This means they’re more likely to spread quickly. Still, some people with sarcomatoid tumors have lived for years thanks to advances in immunotherapy.
Dr. Anna Nowak, a researcher at the Institute for Respiratory Health in Western Australia, says immunotherapy boosts survival. She tells us, “For people with sarcomatoid and biphasic mesothelioma, we can double survival with the combination of ipilimumab and nivolumab.”
Treatment Options for Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma
Sarcomatoid mesothelioma can be treated with chemotherapy, immunotherapy, palliative care and other treatment options. Treatment varies for each person, depending on cancer stage, tumor size and health. The rapid recurrence of this type means surgery is rarely advised. However, it may be an option for peritoneal patients who respond well to immunotherapy.
Recent research shows immunotherapy can offer lasting benefits to some sarcomatoid patients. However, Tumor Treating Fields therapy hasn’t proven effective for sarcomatoid tumors. For the best options, it’s wise to consult a mesothelioma specialist at a top cancer center.
Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma Treatment
- Chemotherapy: Patients with sarcomatoid mesothelioma who receive Alimta plus cisplatin or carboplatin chemo have a median survival of 15 months.
- Immunotherapy: Opdivo and Yervoy, two immunotherapy drugs, improve patient survival an average of 4 months over chemotherapy alone.
- Palliative Care: Less invasive chemo and surgery can ease symptoms and slow tumor growth. They can also improve breathing, thanks to palliative care.
- Radiation Therapy: Often used alongside other therapies, radiation may increase the 2-year life expectancy 30% for some mesothelioma patients.
- Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapies are showing effectiveness for some cancers in clinical trials
“Sarcomatoid mesothelioma is a little less responsive to chemotherapy,” mesothelioma specialist Dr. Andrea Wolf of Mount Sinai Hospital tells us. “But from what we see from more recent data, it may be more responsive to immunotherapy. And we have additional treatment options for those patients.”
Sarcomatoid patients may seek palliative care for symptom relief and better quality of life. Yet, only 48% of the mesothelioma patients we surveyed in 2023 reported using it.

Common Questions About Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma
- Is sarcomatoid mesothelioma curable?
-
Sarcomatoid mesothelioma is generally considered incurable. Surgery isn’t typically recommended for sarcomatoid mesothelioma. Other treatments including immunotherapy, chemotherapy and radiotherapy are unlikely to be curative. There may be occasional long-term survival in sarcomatoid mesothelioma treated with immunotherapies.
Answered By: Anna Nowak, internationally renowned asbestos researcher and mesothelioma advocate
- Where can I get treatment for sarcomatoid cell mesothelioma?
-
You can get treatment for sarcomatoid mesothelioma from a specialist at a top center. This type is harder to treat and needs an expert. Specialists work at the best cancer centers, usually in major cities.
- Can sarcomatoid mesothelioma be prevented?
-
Avoiding asbestos can help prevent sarcomatoid mesothelioma. This exposure often occurs at work or from damaged materials. Wearing personal protective gear and following guidelines can help protect you from occupational exposure. Also if you believe your home may have older legacy asbestos, hire a professional to conduct an inspection and remove it.
- Is there any ongoing research on sarcomatoid mesothelioma?
-
Researchers are working on new treatments for sarcomatoid mesothelioma. Some participants in clinical trials have had success with new immunotherapy drugs. You might qualify for a trial and receive the latest treatment for sarcomatoid cells. So ask your mesothelioma specialist about the best options for you.





